Published on: April 21, 2023 Updated on: February 1, 2024
How AI Image Generators Work: A Beginner’s Guide to AI
Author: Daniel Coombes

In recent years, AI art generators, such as Artflow.ai and DALL-E 2, have been increasingly capturing the minds of internet users around the globe. The ability to create fantastical works of art, or just have some fun, with no artistic ability or Photoshop skills has unlocked the imaginations of millions.
However, very few individuals understand the complex technology behind these innovative apps. So, put down your virtual paintbrush as we peel back the canvas on artificial intelligence and answer the important question: how do AI-generated images work?
How exactly do AI image generators work?
Take a look at the images below of astronauts dining on the moon and try to decipher which one was created by artificial intelligence and which was designed by a human artist.
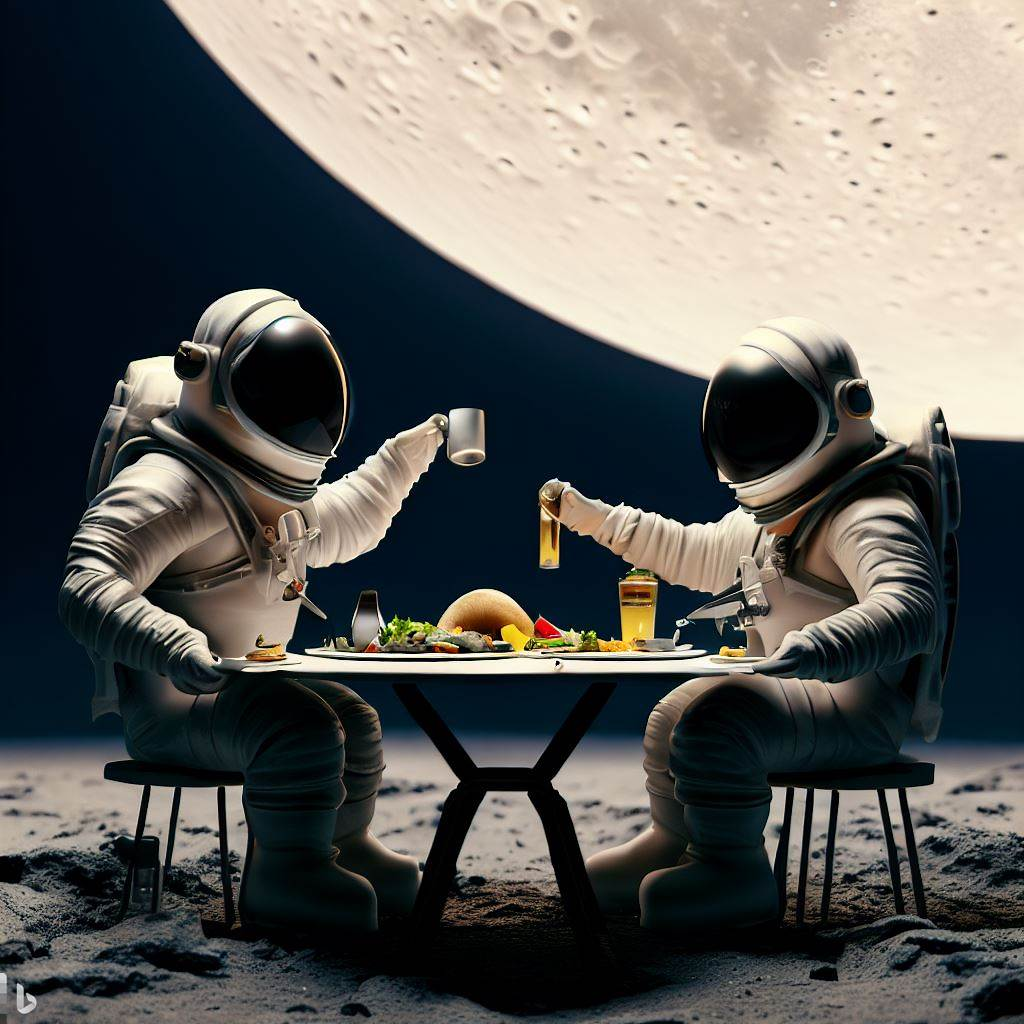
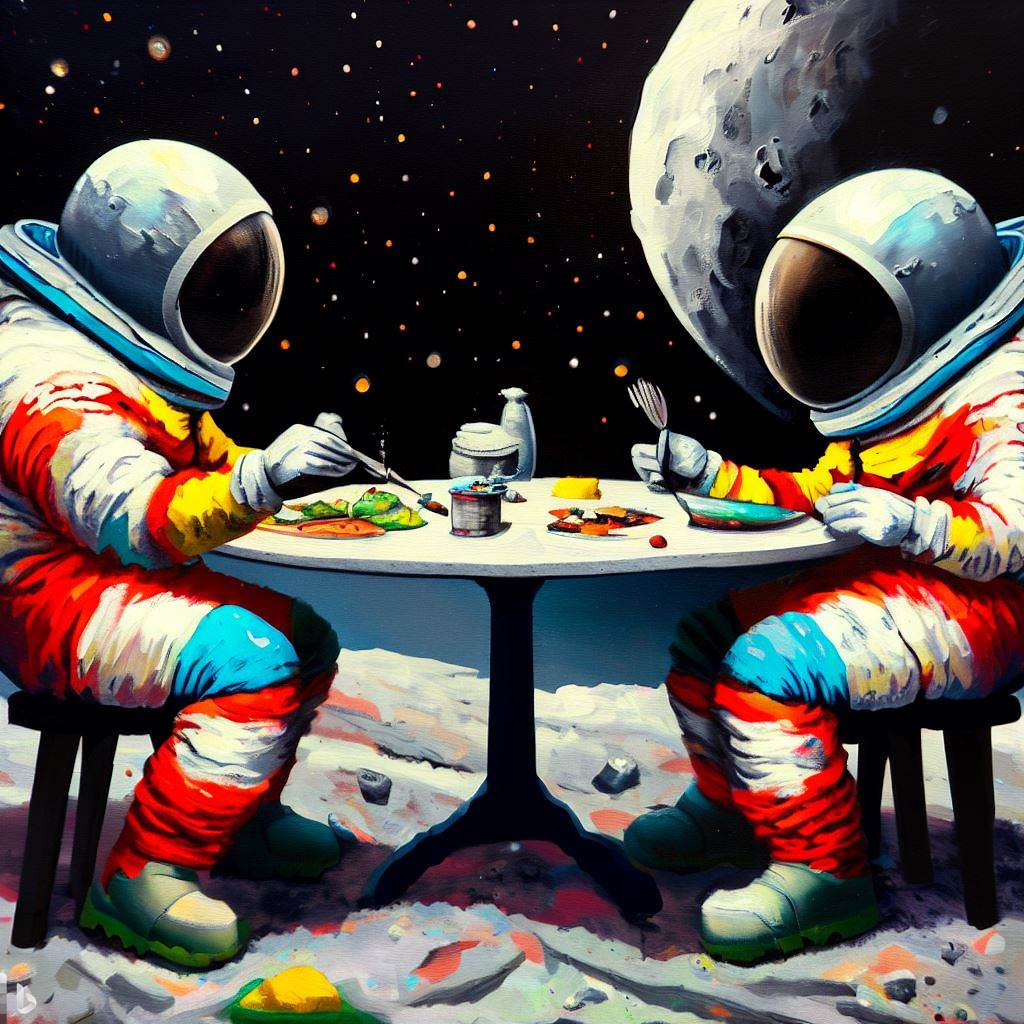


We understand if you are struggling; after all, both are high-quality, beautiful pieces of art that are eye-catching and would look great hung on a wall.
However, it is time to reveal the truth that Bing’s Image Creator actually created both of these images. This is an effective demonstration of the power of AI image generators and their ability to create realistic images.
But how exactly does artificial intelligence create this incredible digital art? On the surface, it would seem to most users that they simply insert a text prompt, and the AI system will quickly generate realistic images. Take a look at how easy it is to create an image using Open AI’s art generator app DALL-E 2 in the below image.
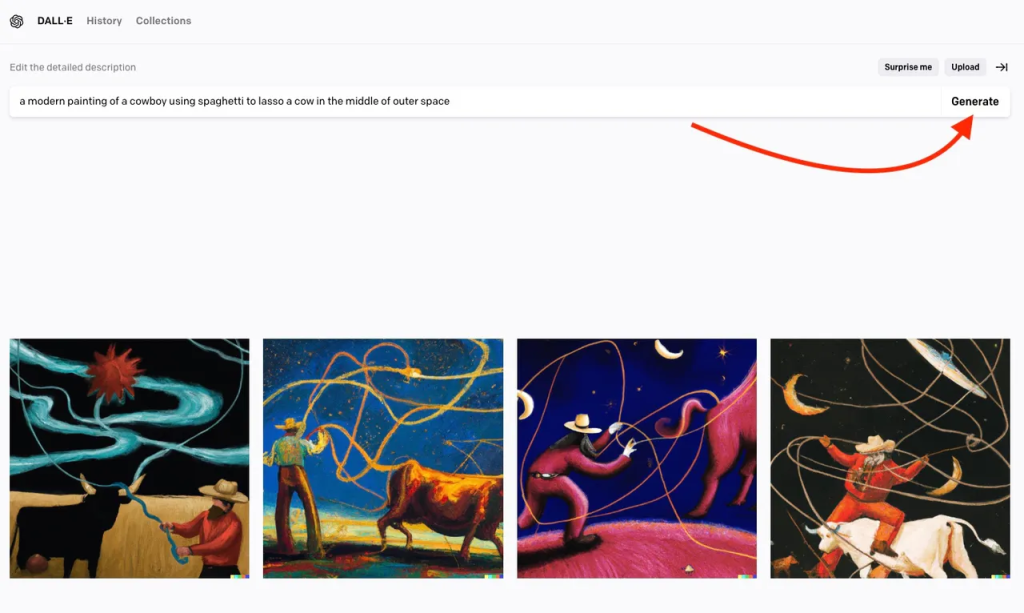
However, behind this simplistic facade is a complicated algorithm that utilizes numerous AI methods that power text-to-image generation. We will now take a look at the most common techniques employed by these artificially intelligent artistic tools.
Generative Adversarial Networks
Earlier versions of these tools, such as This Person Does Not Exist, used Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). These AI models consisted of two competing neural networks: the generator and the discriminator. The generator is asked to create an output of an image that does not exist, which it then tasks the discriminator to figuratively fact-check.
The discriminator is loaded with an endless volume of images, called training data, that it uses to ‘check’ the generated image. This process is repeated in a loop until the discriminator can no longer differentiate the generated image from the real thing.

If we take This Person Does Not Exist as an example, the AI is tasked with generating the face of a fictionalized yet photorealistic person. The generator will continuously produce new images, which the discriminator will compare to a library of real-life people noting any flaws or imperfections. This cycle is repeated until the discriminator is fooled into believing the new image is a legitimate human face.
Neural Style Transfer (NST)
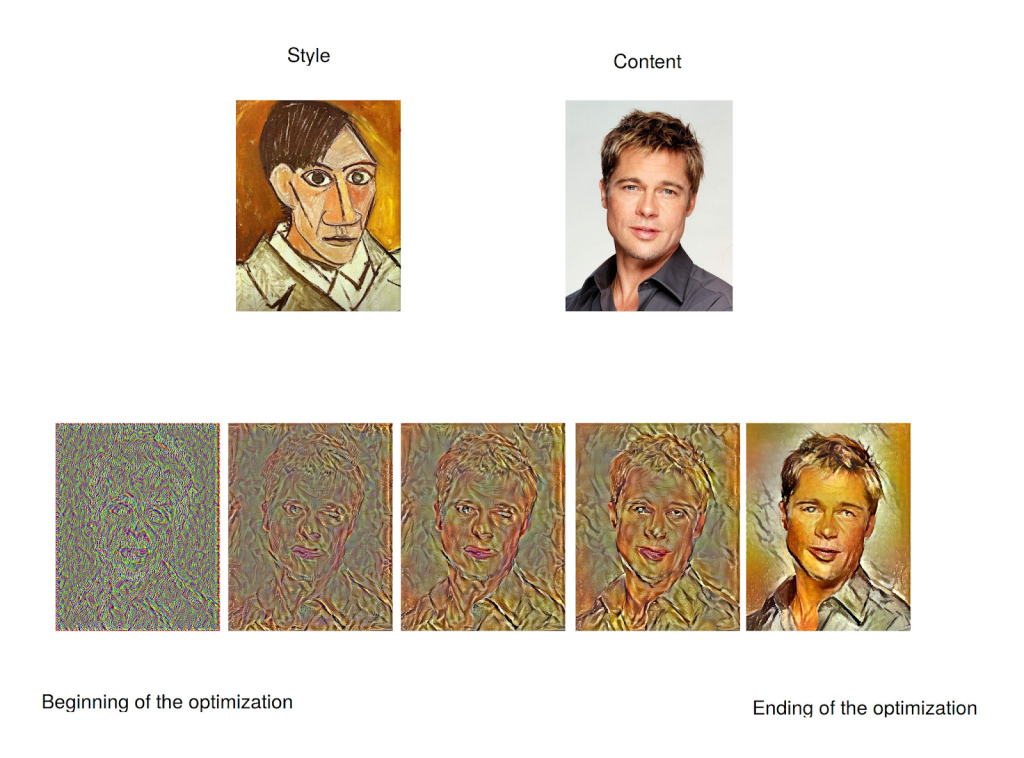
Another method of creating AI-generated art is through Neural Style Transfer seen in such apps as Neuralstyle.art and Prisma. These applications transform original images into different art styles by utilizing deep learning and large datasets.
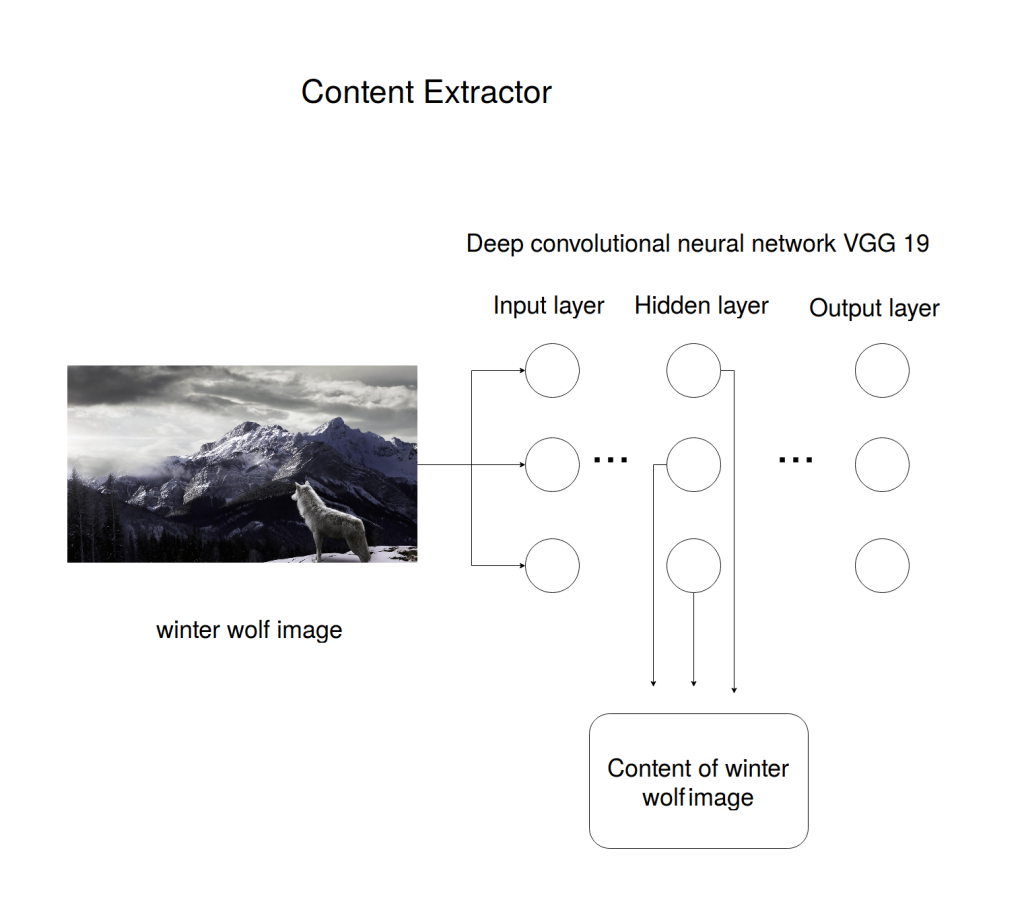
A neural style transfer works by taking both a content image and a style image, which are then merged into a generated output.
A convolutional neural network, a type of AI that mimics human visual capabilities, is used to extract the features and multiple layers of the content image.
Another neural network called the style extractor eliminates the second image’s semantics but retains the basic components and texture.
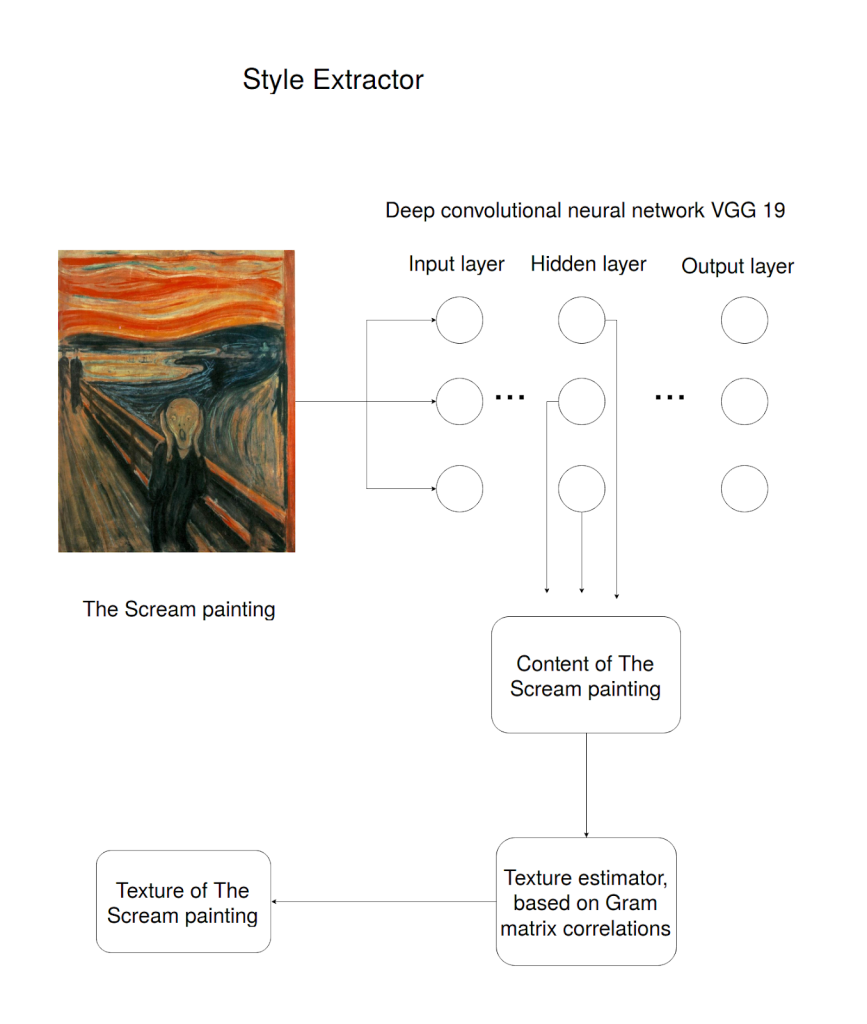
These two outcomes are then processed through a merger that uses a specific cost function. The cost function for this algorithm will penalize a generated image if the content and style are not equal to the inputted images. The AI will then use these datasets in an optimization problem that involves the following:
- The merger creates a white noise image
- Extracts the content and the style from the generated image
- Analyzes the difference between the generated image and the content image
- Defines the difference between the generated image and the style image
- The AI will then measure the overall cost function
- If the result of this procedure is zero, then the optimization process will end
- If the result is more than zero, the AI will create another image with increased similarities to both inputted images
- The process is then repeated until the maximized amount of iterations is reached, or a perfect score is achieved

Diffusion model
The more modern AI art generator apps, such as Stable Diffusion and Midjourney, use a diffusion model to create their wonderful images.
Initially, the diffusion process can seem unbelievably daunting and convoluted. However, we are here to break down this complicated algorithm into an easily digestible format.
The idea of diffusion is innately a scientific one. It is when a substance transforms from a high concentration to a low concentration which is caused by the accelerated movement of particles.
To break down this idea further, imagine placing a drop of red food dye into a glass of water. The food dye particles would soon spread throughout the water, turning it entirely red and changing from high to low concentrations.
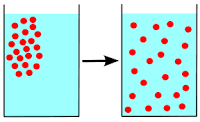
This is the central concept behind generative models. When we enter a text input into a generative AI app, the software will use natural language processing and machine learning to understand this prompt. It will then scour a massive library of stock photos and gather images that have relevant text descriptions.
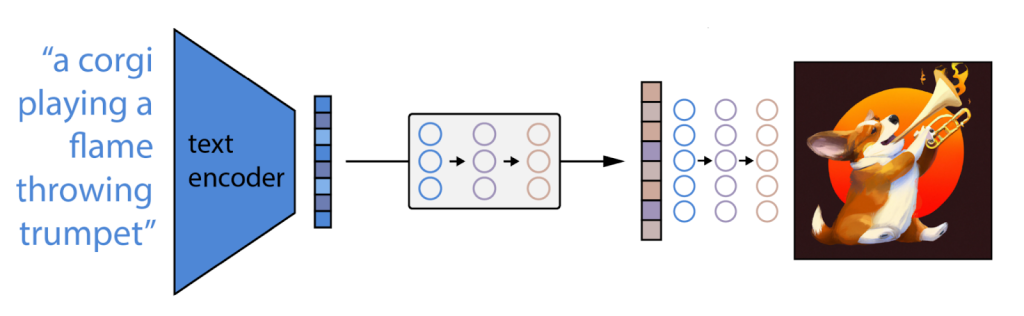
The next step is the diffusion process; the AI takes existing images and diffuses the pixels into noise. The AI model is then tasked with rebuilding the original images using the diffused noise blocks, which will result in a new image.
Pros and cons of artificial art
Now that we have established how artificial art is created, let’s take a look at the pros and cons of this incredible yet divisive emerging medium.
Pros
- Efficiency: The sheer speed at which image generation create works of art is undeniably quicker than a human artist. These apps can create high-quality, detailed images in mere seconds, while an artist can take anywhere between a few days to multiple years to complete a project.
- Variation: There is almost an infinite stream of possibilities and combinations when using AI art generators to create images. This means that budding artists are capable of creating unique art that defies the imagination of the human mind.
- Accessibility: There are millions of individuals out there with wonderful imaginations but are also cursed with an inability to draw. The simplicity of AI art tools allows everyone, no matter their capabilities, to fully unlock their creativity without restriction.
- Cost: A single commission from a human artist will likely cost a business a small fortune due to the materials used and time spent creating the work. However, artificial intelligence art is a mere fraction of the cost, with many tools even offering free credits to generate images.
- Reinvigorating: Many artists admire how AI can repurpose old and forgotten styles into modern artwork. The images generated can be based on classical artists such as Van Gogh and Picasso can be used within prompts to make modern interpretations of their art.

Cons
- Bias: As aforementioned, AI image generator apps are trained on an archive of images sourced from the internet. These images may contain stereotypes, biases, and harmful beliefs that the algorithm will use to create artwork. This means that discrimination could become prevalent in generated content, raising ethical concerns.
- Authorship: The ownership of AI-generated art is a complex one with significant legal ramifications. There are cases to be made for the art being owned by the creator of the algorithm, the user who enters the text prompts, and even the artificial intelligence itself.
- Job loss: A real concern that surrounds the rise of AI-generated art is the potential loss of artists’ jobs. With the incredibly effective and easy-to-use image generators that can mimic any artistic style, the future need for human artists has come into question.
- Human touch: While AI tools are undeniably incredible feats of engineering, they are limited in some regard by their programming. Currently, an AI image generator is unable to replicate true human emotion or thought, which are essential ingredients in creating moving pieces of art.
- Control: When we input a lengthy text description into a generator, we believe that we have some form of control over the output. The reality is that we have very limited control over the final product as artificial intelligence is making almost all the artistic decisions for us.

The legality of artificial art
Karla Ortiza, an incredible concept artist, stated:
“I found a lot of my work there. Almost every artist I know who’s a peer, who’s a professional, who’s been working for a while, whose work is recognizable, was in those datasets.”
One of the biggest talking points of AI image generation is copyright infringement. The immense library of images that AI generative apps use is sourced from the internet and includes numerous copyrighted images.

Elements of these images are then effectively blended and repurposed into new content. The artists behind these archived images are neither contacted for permission nor compensated for the use of their art.
Furthermore, users are able to mimic the artwork of specific artists effectively. For instance, on Stable Diffusion, the artist Rutkowski has been used over 93,000 times to create images in his style. Rutkowski is concerned that his job is in jeopardy, stating that:
“Maybe you and your style will be excluded from the industry because there’ll be so many artworks in that style that yours won’t be interesting anymore.”

However, there are currently no definitive legal standpoints on AI copyright infringement, primarily because copyright law was established before the rise of artificial intelligence. Nonetheless, legal experts claim that an artist’s style can not be copyrighted and, therefore, its recreation is not an infringement. Daniel Anthony, a copyright lawyer, summarizes this best:
“We can replace AI with a human as a thought exercise. If a human reviewed many photos and learned a style of an artist and then produced their own work from scratch in that style, it is not an infringement.”
As of now, we can categorically confirm that AI art is indeed a legal medium, but this could change as the world quickly adjusts to the integration of artificial intelligence in society.
Is AI art an art form?
Artificial intelligence art is rapidly becoming a bonafide medium in the art world, with numerous users from around the globe creating outstanding images rivaling human art.
However, countless individuals have dismissed AI art as a mere fad that mocks true artistic integrity. Legendary anime director and animator known for his with Studio Ghibli stated:
“I would never wish to incorporate this technology into my work at all. I strongly feel that this is an insult to life itself.”
Nevertheless, in recent years there have been countless news stories that have solidified the legitimacy of AI art as a true art form, which include:
- The Portrait of Edmond Belamy was created using an AI algorithm and sold for an incredible $432,000 at auction.
- The iconic Cosmopolitan magazine used DALL-E 2 to generate the first AI-designed cover image.
- Dead End Gallery, located in Amsterdam, was the first art gallery in the world to physically exhibit AI art.
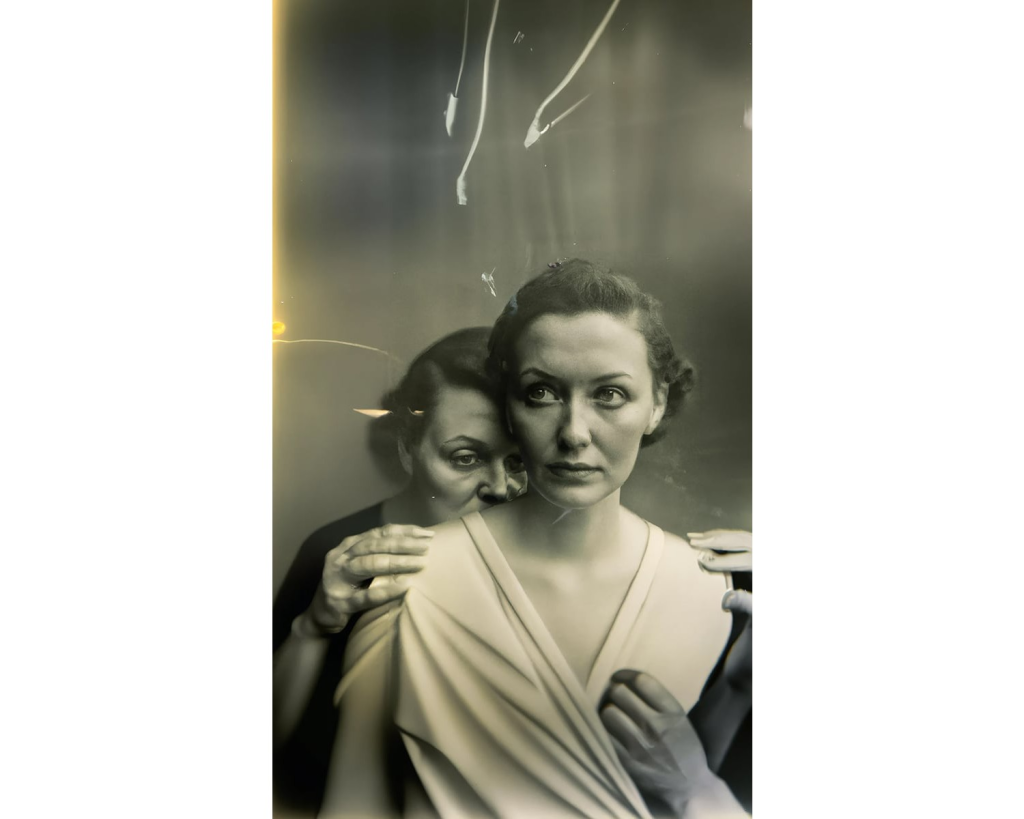
- The winner of the Sony World Photography Awards titled ‘The Electrician’ was revealed to be AI art.
- A digital artist used an AI generator to take home first prize at the Colorado State Fair’s art competition with the image ‘Théâtre D’opéra Spatial’.
Below is the aforementioned AI generated photograph ‘The Electrician’ that won the prestigious Sony World Photography Awards.

The top AI art apps
If our deep dive into the inner workings of AI art has piqued your interest, then check out these incredible artificial intelligence art generator apps now to see the algorithms in action.
- Deep Dream Generator
- DALLE-2
- Jasper Art
- NightCafe
- Craiyon
- Dream AI
- Stable Diffusion
- Midjourney
- DeepAI
- Bing image creator
Artists of the future
Now we have found the answer to the question of how do AI-generated images work, it is time to find out how AI art generators can benefit your business. These incredible tools have an endless amount of use cases, including:
- Fill your social media feed with interesting imagery
- Efficiently create concept art
- Deliver high-quality logos
- Enhance and edit existing images
- Provide exceptional website design and user interfaces
- Create attention-grabbing marketing material and advertisements
- Develop a prototype of a product
However, it is the future of this art medium that is truly exciting; as AI makes strides forward toward more advancements, the scope and capabilities of image generators will only increase. As David Holz, CEO of Midjourney, states:
“It’s really just been an incredible time of discovery. Most startling is the realization of how much further the technology can still go. I think we’ll see more aesthetic exploration over the next three years than the past 200 years.”
Take a look at the many incredible apps in our extensive library now to find the perfect AI art generator for your business.
Daniel Coombes
Daniel is a talented writer from the UK, specializing in the world of technology and mobile applications. With a keen eye for detail and a passion for staying up-to-date with the latest trends in the industry, he is a valuable contributor to TopApps.ai.
Recent Articles

Discover the top apps designed to gamify housework, turning daily chores into a fun experience for the whole family. Track tasks, earn rewards,...
Read More
Discover all the ways you can incorporate selective motion into your Midjourney images using our step-by-step guide. Imagine what you’ll create assisted by...
Read More
ChatGPT can be used for anything, including travel. In this guide, you'll learn how to get the absolute best results from AI when...
Read More